Phytoplankton Productivity
Be sure to write about what you are learning in the lab section of your notebook. You will be expected to answer questions about the lab activity during the lab self test and lab quiz. It helps to have your text and coloring books open beside you for support.
| Refer to the Assigned Readings Below: | |
| Marine Biology Textbook | Chapter 15, pages 343 to 351 |
| Marine Biology Coloring Book | none |
|
Studying Ocean Color |
|
|
Answer the fill-in the blank questions below by visiting the Studying ocean color from space website. |
|
| Questions | Answers |
| 1. Satellites circling the Earth can measure the sea's _____. | |
| 2. Using instruments that are more sensitive than the human eye, we can measure carefully the fantastic array of colors of the ocean. The different colors may reveal the presence and concentration of _____. | |
| 3. Phytoplankton, as revealed by ocean color, frequently show scientists where _____ provide nutrients for plant growth. | |
| 4. During photosynthesis phytoplankton remove carbon dioxide from sea water, and release oxygen as a by-product. This allows the oceans to absorb additional carbon dioxide from the atmosphere. If fewer phytoplankton existed, _____. | |
| 5. The concentration of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere has changed in the past hundred years. _____ provides one of the many tools scientists use to try to find what changes are occurring, and how they may affect us. | |
|
The SeaWiFS Project |
|
|
Answer fill-in-the-blank questions below by visiting the Background on the SeaWiFS project website. |
|
| Questions | Answers |
| 1. The purpose of the Sea-viewing Wide Field-of-view Sensor (SeaWiFS) Project is to provide quantitative data on global ocean _____ to the Earth science community. | |
| 2. The concentration of microscopic marine plants, called phytoplankton, can be derived from satellite observation and quantification of ocean color. This is due to the fact that the more phytoplankton present, the greater the concentration of plant pigments and the _____ . | |
| 3. Ocean color data have been deemed critical by the oceanographic community for the study of ocean _____ and global biogeochemistry. | |
|
Phytoplankton Concentrations |
|||||||||
|
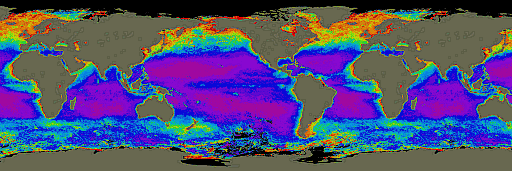
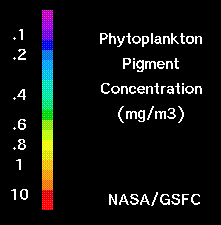
Answer the questions below by exploring the world map displaying phytoplankton concentrations in all of the worlds oceans. Use the legend below the map for an explaination of the map colors. |
|||||||||
|
|
|||||||||
|
|||||||||
Lab Activity 11.3 Planktonic Animals